ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
The Orthognathic Surgery Department is dedicated to the diagnosis and surgical treatment of changes in adult facial bone development.
Orthognathic surgery is an intervention that corrects dentofacial asymmetries in order to achieve a perfect balance of the face and teeth. Dentofacial dysmorphias are quite common in the general population.
What is orthognathic surgery?
Orthognathic surgery is the surgical field responsible for correcting dentofacial deformities with the aim of achieving a harmonious balance between the face and the teeth.
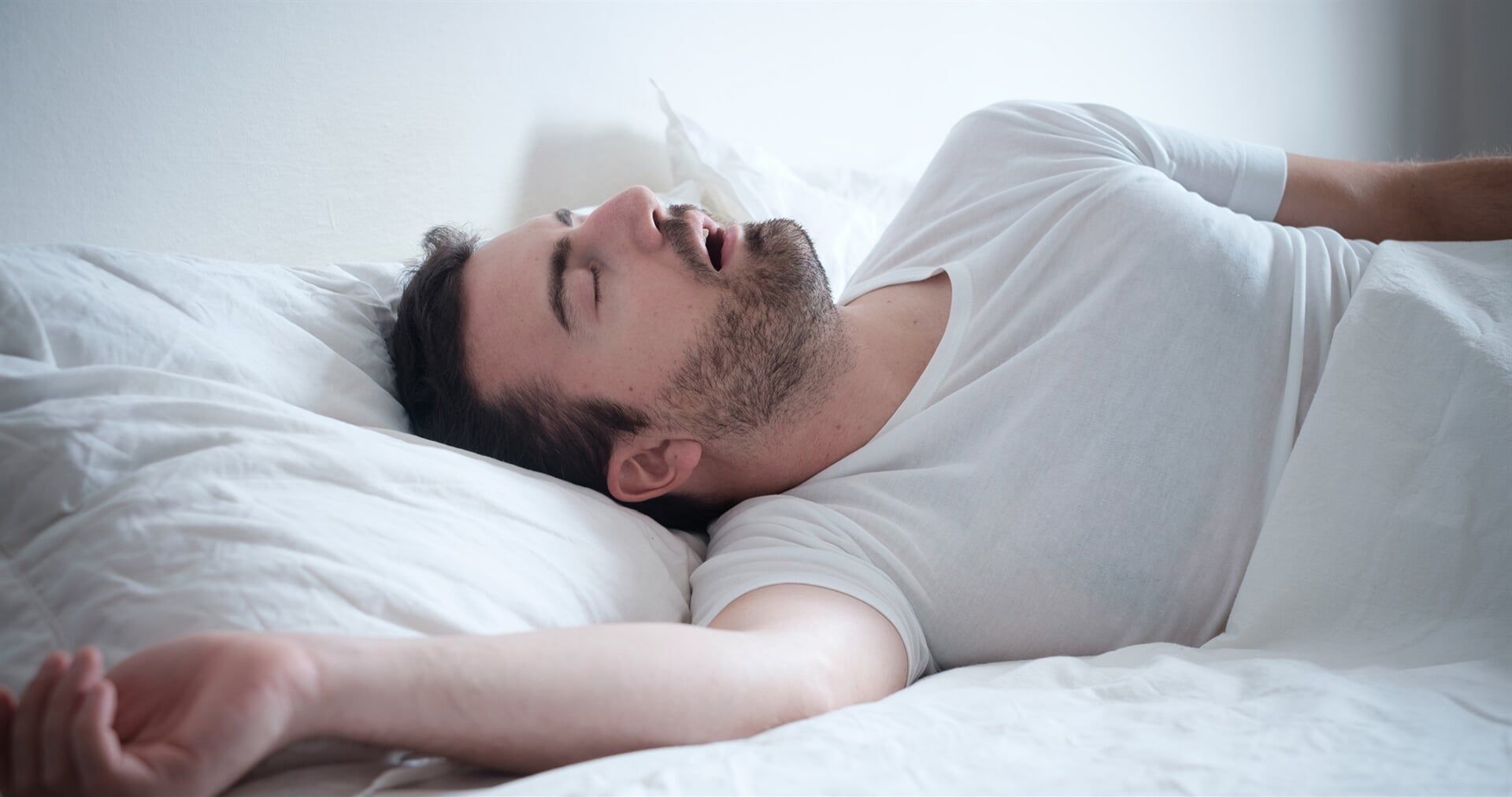
After a variable period of orthodontic preparation, the intervention is performed on the jaws to achieve harmony between all the patient's facial features, along with correct occlusion and improved breathing (allowing for greater airflow through the upper airway).
As the position of the jaws is altered forward, backward, upward, or downward, the soft tissues also move with them, meaning the chin, lips, cheeks, or the tip of the nose. Thus, once the jaw is placed in the correct position, the facial profile becomes correct, producing harmony with the new facial features.
THE ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
DENTOFACIAL DEFORMITY
- Mandibular prognathism or "big chin"
- Retrognathism or "small chin"
- Gingival smile or "gummy smile"
- Open bite or "front upper and lower teeth that slant outwards"
- Cross bites and facial asymmetry or "crooked or deviated face"
Often, patients recognize that they have asymmetries in the face, such as a deviated chin, which results in a significant aesthetic compromise.




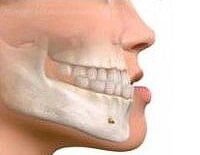
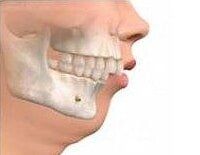
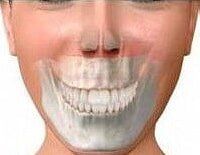
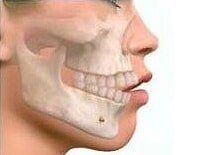
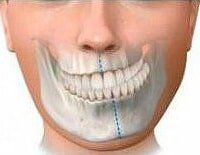
MANDIBULAR PROGNATHISM
MANDIBULAR RETROGNATHISM
GINGIVAL SMILE
OPEN BITE
CROSSBITE
These bone changes result in an incorrect position of the teeth, with a negative impact on facial harmony/aesthetics. These can be treated in isolation or associating various aspects, creating an individualized treatment plan to obtain the best functional and aesthetic result in each case of orthognathic surgery.
Treatment with orthognathic surgery is a procedure that always includes associated orthodontic treatment before and after surgery. After orthognathic surgery, intensive rehabilitation treatment is always necessary.
Changes in the length, width or height of the jaw result in difficulty in accommodating the teeth as well as changes in the relationship between the upper and lower teeth. The teeth try to adapt to this lack or excess of bone, adopting positions different from those they would have if the structure were correct. Excessive showing of the gums when smiling, inability to completely bring the lips together effortlessly, not showing the upper teeth when smiling, jaw back, jaw forward, crooked teeth in the jaw, facial asymmetries, chin back, chin forward, are some of the main complaints of our patients. These problems, being of the jaws and teeth, must be treated together with Orthodontics (to decompensate the adopted position) and surgery (to put the jaws in the correct position), otherwise this could give to unsatisfactory final results, indefinite and recurrent orthodontic treatments, with patients often experiencing asymmetries on the face, for example, a deviated chin with important aesthetic implications.
MAIN CAUSES
The causes that lead to the manifestation of dentofacial deformities can come from:
Hereditary Factors
These are problems of genetic origin, meaning the malformation results from a change in the genes or a characteristic passed down from generation to generation.
Congenital Factors
These factors are anomalies developed during the intrauterine formation period. They mostly occur due to the ingestion of medications or drugs during pregnancy, as well as nutritional deficiencies or hormonal disorders.
Acquired Factors
Acquired factors include dental problems, oral infections, trauma, or poor oral hygiene. A diet low in fiber, lack of stimulation caused by breastfeeding, and bad habits such as prolonged use of pacifiers or thumb sucking can also be the source of these deformities.
Diagnosis
The changes caused in the jaws, such as length, width, or height, can result in difficulties in the positioning and/or alignment of the teeth and also in the alteration of the relationship between the upper and lower teeth. The teeth try to adapt to this lack or excess of bone, adopting positions different from those they would have if the structure were correct.
Excessively showing the gums when smiling, being unable to close the lips completely without effort, not showing the upper teeth when smiling, a jaw pushed back or forward, crooked teeth in the upper jaw, facial asymmetries, a receding chin, and a protruding chin are some of the main complaints of patients.
Treatments
Orthognathic surgery is closely related to orthodontics. Typically, treatment begins with the extraction of wisdom teeth, followed by an orthodontic treatment prior to surgery that lasts between 1 to 2 years, in cooperation with the orthodontist. This time can be shorter, depending on the case.
In specific cases, orthodontics may not be necessary prior to surgery.
At the Portuguese Institute of the Face, all orthognathic surgeries are planned virtually, allowing for a more predictable and precise result with more accurate surgical movements and a faster post-operative recovery.
TYPES OF ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
MAXILLARY SURGERY (Le Fort I Osteotomy)
What is it?
Maxillary orthognathic surgery is performed to correctly position the maxilla to achieve facial harmony and, most importantly, to restore the functionality of this bone, which is key for chewing, breathing, and speaking.
Who should undergo it?
This procedure is performed to correct various facial deformities, such as maxillary deficiency, mandibular prognathism or Class III, open bite, or gummy smile.
How is it performed?
Maxillary orthognathic surgery involves making a cut in the maxillary bone called a Le Fort I osteotomy, which allows for the advancement, retrusion, elongation, shortening, or rotation of this bone. Once in the desired position, the maxilla is fixed with titanium plates and screws, a material that is completely biocompatible.
JAW SURGERY (BSSO type osteotomy)
What is it?
Mandibular surgery can be performed for two reasons: in cases of patients with a small or retruded jaw in relation to the skull – a condition known as retrognathia or Class II – or in cases of mandibular prognathism or Class III, where it is necessary to move the jaw back.
Who should undergo it?
This procedure is recommended for patients who have this type of malformation that especially affects the harmony of the lower third of the face and causes various functional problems, including sleep apnea.
How is it performed?
Mandibular surgery consists of making a cut on each side of the jawbone, called bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (BSSO), followed by the movement of the bone forward or backward and then fixing it in the new position with titanium plates, a completely biocompatible material.
MAXILLOMANDIBULAR OR BIMAXILLARY SURGERY
What is it?
In most patients with dentofacial alterations, it is necessary to reposition the maxilla and mandible to achieve correct occlusion and facial harmony. This procedure is known as maxillomandibular surgery or bimaxillary orthognathic surgery.
Who should undergo it?
Bimaxillary orthognathic surgery is recommended to treat the following malformations: Class II, Class III, facial asymmetry, open bite, among others, when a single-jaw surgery is not sufficient to achieve the desired result.
How is it performed?
The surgery does not leave external scars because it is performed through incisions inside the mouth, which take about ten days to heal, with the stitches being absorbable. In terms of final bone healing, the mandible typically consolidates in 2 months, and the maxilla consolidates in 4 months.
During the first 3 months after surgery, several sessions of physiotherapy and speech therapy will be carried out, along with follow-up from the surgeon, to ensure better functional recovery.
MENTOPLASTY
What is it?
Mentoplasty, also known as genioplasty, is a surgery that allows the alteration of the shape, size, and position of the chin to harmonize the facial profile.
Who is it for and how is it performed?
This surgery is performed through a small incision inside the mouth (leaving no external scar), allowing movements such as increasing or decreasing the chin bone, as well as repositioning or rotating it. In specific cases, a custom-made prosthesis can also be used to achieve the desired facial aesthetic result.
These techniques provide a permanent result for the patient. One of the major advantages of mentoplasty is its relatively light post-operative recovery compared to other aesthetic surgeries, with visible results in a short amount of time.













