TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DYSFUNCTION
Department of Orofacial Pain and Temporomandibular Dysfunction."
The Orofacial Pain and Temporomandibular Dysfunction Department of the Portuguese Institute of the Face is dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis, education, treatment, and rehabilitation of conditions associated with facial pain.
OROFACIAL PAIN ('FACIAL PAIN') CAN HAVE DIFFERENT ORIGINS
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
Myalgia
Neurovascular Pain
Neuropathic Pain
Headaches
Migraines
Oral Origin Pain
Since this pain can have different origins, a multidisciplinary approach is essential—specialists in temporomandibular dysfunction, maxillofacial surgery, stomatology, neurology, otorhinolaryngology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, oral medicine, physiotherapy, and speech therapy.
WHAT IS THE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT?"
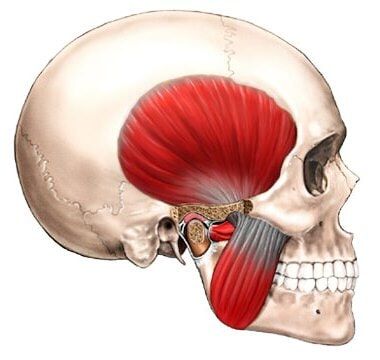
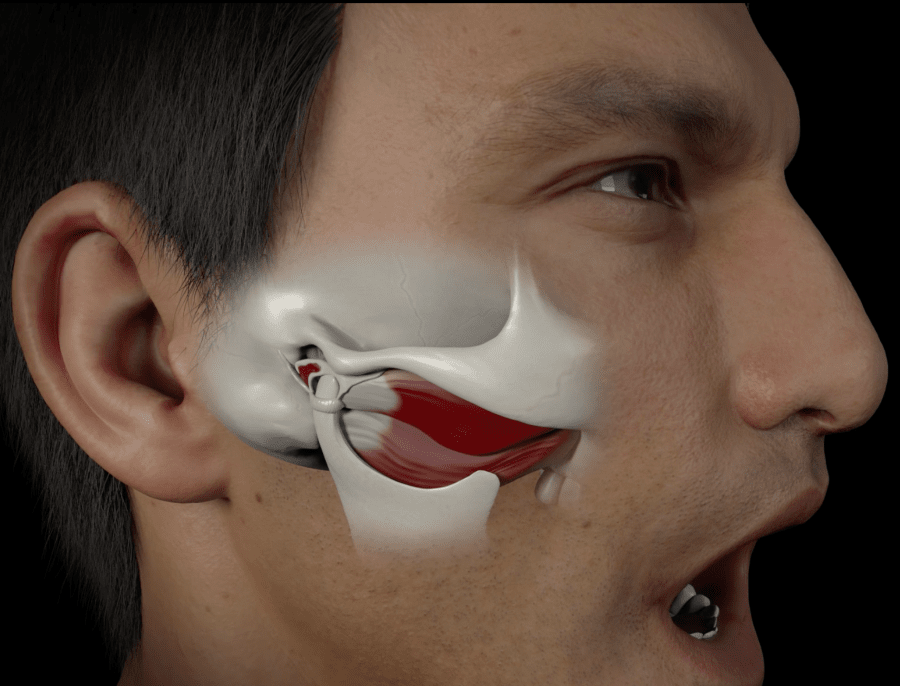
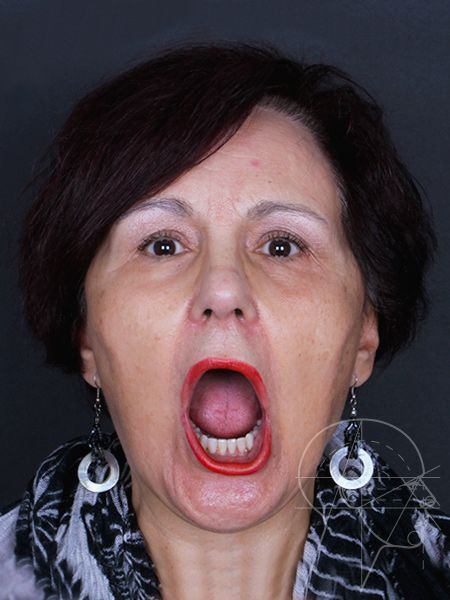
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located near the ear and is used to perform essential activities of our daily lives, such as eating, speaking, smiling, and yawning.
When this joint has a pathology, we can say that we have temporomandibular dysfunction (TMD).
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DYSFUNCTION
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
WHAT ARE THE MOST COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DYSFUNCTION?
Do you feel pain in your face and/or in the joint (often confused with earache), joint snap, blockages, or limitation in opening your mouth?
Do you have a sensation of jaw dislocation, some muscle or neck tension, a feeling of ‘grit’ in the joint, and headaches?
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, it is recommended to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists.
MAIN CAUSES
WHAT ARE THE MAIN CAUSES OF TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DYSFUNCTION?
The origin of the pathology is often related to:
- Acute trauma
- Chronic trauma
- Autoimmune pathology
- Benign or malignant tumors
- Bruxism (teeth grinding) - often associated with stress/anxiety
- Dental clenching - often associated with stress/anxiety
DIAGNOSIS
HOW IS THE DIAGNOSIS OF TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DYSFUNCTION PERFORMED?
In the initial phase, it is essential to interpret the patient's clinical history and conduct an appropriate objective examination to formulate some diagnostic hypotheses.
After the first consultation, our specialists in Orofacial Pain and Temporomandibular Dysfunction may need to request some exams, such as: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the temporomandibular joints and/or; Computed Tomography of the temporomandibular joints.
We highlight the two most important muscles in chewing: the masseter muscle and the temporal muscle.
OTHER COMMON PATHOLOGIES THAT CAUSE ORAL-FACIAL PAIN
TREATMENTS FOR TEMPOROMANDIBULAR PAIN
Pharmacological Treatment
The specialized medical team may prescribe medications to control some of the symptoms - anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, antidepressants, and/or antiepileptics.
NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
The use of relaxant drops/plates, physiotherapy, or acupuncture may be prescribed to manage your symptoms.
PROTOCOL WITH BOTULINUM TOXIN FOR THE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DEVELOPED BY IPFACE
O IPFACE desenvolveu um protocolo exclusivo para o tratamento da Disfunção Temporomandibular de origem muscular, com toxina botulínica e fisioterapia. Este protocolo permite o controle da dor muscular, relaxar toda a musculatura cervicofacial e reeducação muscular.
Neste momento a equipa do Instituto Português da Face tem mais de 900 doentes tratados com este protocolo, com uma taxa de complicações inferior a 0.13%, e uma taxa de sucesso global próxima dos 83%. A taxa de satisfação global dos doentes que realizaram este tratamento é de 7.05 ± 2.90 (1-10) em 22 doentes aleatórios.
PSYCHOTHERAPY
According to the holistic perspective of modern medicine, it is essential to treat patients as a whole - body, mind, and spirit - thus, in some cases, psychotherapy sessions may be recommended.
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Special techniques of kinesiotherapy, manual massage, and muscle strengthening may be recommended, specifically for the temporomandibular joint.
SPEECH THERAPY
Functional rehabilitation of the stomatognathic system with physiotherapy exercises may be recommended.